Alkaline earth metal magnesium is one of the main components of the life of the human body. Its task is to activate the work of B-group vitamins and enzymes.
He takes part in metabolism, protein and carbohydrate metabolism. The magnesium content in foods allows you to provide support for a healthy state, if these foods are consumed correctly and in the right amount.
Magnesium in the body: normal and deficiency
The correct balance of magnesium with potassium, calcium and sodium is extremely important. The health of the skeletal and cardiovascular systems of the body, the correct muscle activity and the psychological state depend on this.
On the recommendation of medical specialists, the daily dose of magnesium should be 400 mg. For pregnant women, it increases to 450. The daily need for magnesium varies depending on the age of the child: from one to three years - 80-85 mg, from four to eight years - from 120 to 140 mg, from nine to thirteen years - about 250 mg
On its own, an element in the body is not produced, so you can replenish its amount by consuming food products, in which most of all magnesium. With a sharp deficit of the substance, you can resort to taking specially developed vitamin-mineral complexes.
Magnesium deficiency can be caused by the following factors:
• mismatch of the intake of a substance into the body and its costs. This condition is observed in pregnant women, people who are actively involved in sports, people engaged in heavy physical activity;
• constant nervous tension and regular stress;
• long-term antibiotic therapy;
• chronic dysbiosis. With this diagnosis, the natural absorption of all nutrients is impaired;
One of the main signs of metal deficiency is rapid fatigue, unmotivated irritability (sometimes aggressiveness). In addition, nervous and muscle excitability increases. Since magnesium affects bone strength, the risk of fractures and the development of arthrosis and osteoporosis increase with its lack. Other symptoms of insufficient metal:
• tachycardia and arrhythmia;
• fatigue;
• restless sleep;
• headaches, dizziness (rarely - fainting);
• forgetfulness and inattention;
• depressed state, depression;
• low hemoglobin level;
• night cramps of the lower extremities;
• unhealthy appearance, dry hair;
• brittle nails;
• loss of appetite, sometimes accompanied by nausea;
• unreasonable anxiety.
You should know that (hypermagnemia) an excess of magnesium is also dangerous to health. This can cause malfunctions in the thyroid gland and the nervous system. The cause of excessive magnesium can be uncontrolled medication.
Positive effect of magnesium in food
Regular intake of magnesium in food products ensures the stable functioning of organs and systems. The main useful qualities of metal are:
• prevention of cancer;
• stabilization of carbohydrate metabolism;
• maintaining the correct balance of blood sugar, and diabetes prevention;
• maintaining healthy bones;
• strengthening the nervous system, increasing stress resistance;
• regulation of pressure and heart rate;
• prevention of urolithiasis and gallstone disease;
• mobilization of the body's defenses and increase immunity;
• elimination of excess cholesterol;
• prevention of fatigue;
• stabilization of the pancreas.
A sufficient amount of magnesium in food will ensure the full functioning of the organs and systems of the body.
Which foods have the most magnesium?
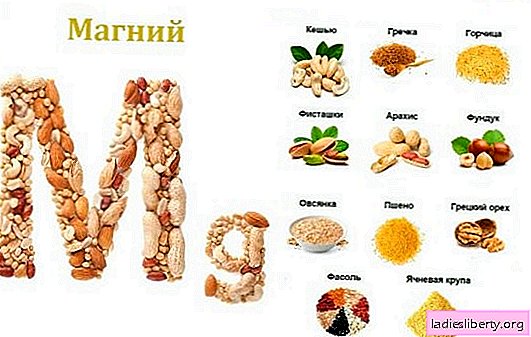
The main source of magnesium is foods of plant origin. This metal is found in large quantities in nuts, bakery products, bran, seafood and cereals.
To answer the question in which products the most magnesium, you can compare their characteristics.
Per 100 grams of product contains the following amount of chemical element:
• wheat bran - 580 mg;
• sea kale - about 800 mg;
• cocoa - 425 mg;
• nuts: cashews, cedar, almonds, pistachios, peanuts, hazelnuts - 270 mg, 230 mg, 225 mg, 200 mg, 175 mg, 169 mg, respectively;
• sesame - 325 mg;
• beans and buckwheat - 260 mg each;
• watermelon - 225 mg;
• cereals: oat and barley - 140 mg each;
• wheat and beans - about 135 mg;
• green peas (not canned) - 100 mg;
• bran bran - 93 mg;
• parsley and dates - 85 mg each;
• lentils and spinach (fresh) - about 80 mg;
• dill and rye bread - 70 mg each;
• rice groats - from 64 to 160 mg (depending on the rice variety);
• hard cheeses - about 60 mg;
• prunes, arugula, feckhel, chicken eggs - approximately 47 mg;
• carrots, bananas, chicken - up to 37 mg;
• raisins, garlic - 30 mg;
• meat: pork and beef - 28 mg;
• bananas and broccoli - up to 25 mg;
Some useful tips
Having decided which foods contain the most magnesium, and having selected them for your diet, you should not eat them uncontrollably. And also rape the body with food that does not cause pleasant emotions.
Nuts are not recommended to be used excessively because of their hard digestibility by the digestive tract. It is desirable to alternate cereals from cereals enriched with magnesium. Preference should be given to the morning reception of this dish. Sweet corn flakes will not be an alternative to conventional ones. Therefore, as a source of magnesium, cereals without sugar should be chosen.
Seaweed is an amateur product. To get out of this situation, recipes for a variety of salads with the addition of this seaweed will help. Options for healthy and delicious canned seaweed dishes:
Salad Ingredients
• Sea cabbage, white cabbage, red cabbage, cucumbers: fresh and pickled, green onions, fresh dill, salt, ground black pepper.
• Seaweed, fresh vegetables and herbs: cucumber, cherry tomatoes, red onions, dill. Pickle, black pepper, salt.
• Seaweed, boiled eggs, vegetables: onions, fresh cucumber, sweet pepper, sea cocktail or crab meat (sticks can be), boiled friable rice.
• White cabbage and sea cabbage, spicy Korean carrot (prepared or cooked independently), dill, salt.
Salad dressing
• Mix natural 2% yogurt (without additives) with lemon juice. Alternatively, you can use mayonnaise.
• Mix olive oil with balsamic vinegar in a ratio of 3: 1
• Light mayonnaise with a small percentage of fat content.
• Vegetable or olive oil, a little lemon juice.
How to make up for the lack of magnesium in food
To eliminate the deficiency of a chemical element in the body, one can resort to the use of medical medicines containing magnesium: magne B6, magnistrat, magnelis B6, systematics magnesium + B6, magnnerot. Contraindications to the use of all drugs: chronic kidney and liver diseases.
Important! Do not self-medicate. The use of medicines is permissible only with the permission of the doctor, after a preliminary analysis of the amount of element in the body.